Nearly half of engagement ring center stones (46%) sold in 2023 were lab-grown, according to a survey by The Knot.1 Buyers like that these very real diamonds are a fraction of the price of natural stones and more ethically sourced.
However, a low retail price comes with a much lower resale value, and it is hard to resell these increasingly ubiquitous, and low-cost diamonds, which today fetch as little as 20% of the retail value — if you can find a buyer at all.
Keep reading to learn more about lab-grown diamonds and what they’re worth on the resale market, plus some of the places where you can sell:
Can you sell lab-grown diamonds?
Where to sell lab-grown diamonds at the best price
- Pawn shops
- Online lab-grown diamond buyers
- Direct to buyers
- Jewelry consignment
- Sell lab-grown diamond “near me”
How to sell lab-grown diamonds
Bottom line: Understand the value of your lab-grown diamond before you sell
Can you resell a lab-grown diamond?
It is possible to resell lab-grown diamonds, though technological efficiencies adapted from industries like solar power and 3D printing have made lab-grown diamonds easier to make and therefore less valuable than even a few years ago.
This means that it is not profitable for most diamond buyers or jewelers to buy your lab-grown diamonds.
Diamonds USA, with an A+ Better Business Bureau rating does buy all sizes of lab-grown diamonds, and Worthy.com, also with a Better Business Bureau rating of A+, buys lab-grown synthetic diamonds of at least 3 carats.
What is the resale value of lab-grown diamonds?
The decrease in value for a lab-grown diamond is much greater than natural stones. Expect to get about 50% of today's retail value for your natural diamond, vs. about 20% to 40% for a LGD.
Diamonds USA is one of the few diamond buyers that does buy all sizes of lab-grown diamonds and shares this chart to help sellers understand the resale market of both natural and lab-grown diamonds. Both are worth more if you have a GIA certificate validating the stone's qualities:
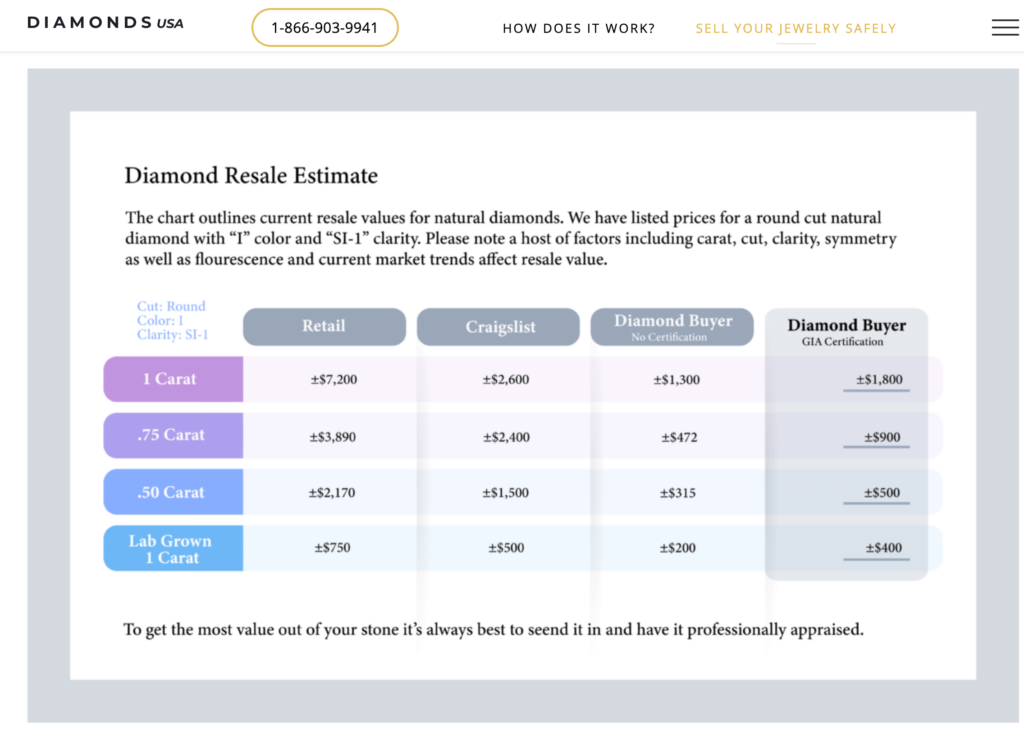
According to Diamonds USA, a 1-carat lab-grown diamond that you buy today for $750 could be sold on Craigslist for about $500, or $200 to a diamond buyer — or about $400 if you have a GIA certificate.
Where can I resell lab-grown diamonds for the best price?
Few diamond buyers will buy used lab-grown diamonds, though that is changing. Diamonds USA and Worthy.com both buy lab-grown diamonds.
The easiest way to start the LGD resell process is to start by checking with the original jeweler where your ring was purchased to see if they have a buyback or exchange program. If that fails, here are some other options:
Pawn shops
If you need quick cash, a quality local pawnbroker may be a good option, with a transaction that can take 15 minutes or less. Learn more about what your local pawnshop buys and how to find a quality pawn shop in your community.
Online lab-grown diamond buyers
First, understand what your stone is worth. Again, lab-grown diamonds are graded the same as natural stones, so collect any documentation of what you own, including the gold or platinum setting.
In fact, the precious metals are likely worth as much or more than the lab-grown diamond. While the retail and resell value of both natural and lab-grown diamonds is declining, gold prices have remained strong in recent years.
Search for online reviews on Yelp, Google Business, Better Business Bureau and TrustPilot.
Two places to sell your LGD online that we partner with are Worthy and Diamonds USA:
| Diamonds USA | Worthy.com |
| A+ Better Business Bureau | A+ Better Business Bureau |
| Insured up to $150,000 | Insured up to $100,000 |
| Free, trackable shipping | Free, trackable shipping |
| ~3 days total from requesting mailer to payment | ~2 weeks from requesting mailer to payment |
| No minimum size | 3 carat minimum |
| Buys direct | Auction |
| Also buys gold, silver, flatware, watches and all sized diamonds | Specializes in large diamonds and branded jewelry like Tiffany and cartier |
Read our review of CashforGoldUSA, Diamonds USA's sister company, and a review of Worthy.com.
Or get a quote from Diamonds USA now.
Direct to buyers
Whether you post on Facebook Marketplace, ebay, Craigslist or another resale site, you can set your own price and try to find a buyer willing to pay it.
On ebay, you can browse other lab diamond listings to get a sense of successful sales prices.
Sellers successful with jewelry sales on these platforms tend to have a large volume of products and professional photography equipment, though you may have luck if you price your diamond right.
Jewelry consignment
You might also try selling lab diamond jewelry at local or online consignment shops like Louped, and Poshmark. Another option is Mercari, a peer-to-peer secondhand marketplace. Keep in mind, most successful sellers on these platforms have built large retail platforms over long periods.
Sell lab-grown diamond “near me”
Local jewelry stores, pawn shops, jewelry stores, and consignment shops near you may buy pre-owned lab-grown diamonds. While there are very few places that do buy lab-grown diamonds, it can be worth a quick search to see if anyone in your community is buying them:
How to sell lab-grown diamonds
If you do intend to sell your lab-grown diamond, there are a few things to keep in mind to ensure you do not get ripped off and get the most money for your jewelry — no matter how low the value may be:
The first step in selling a lab-grown diamond is to understand its value. Gather any receipts, lab reports or any other documentation about your lab-grown diamond and its setting.
Because lab diamonds are less likely to have imperfections than natural ones, carat is the most important factor in determining the value of your rings. Larger carat stones tend to come with a higher value.
A GIA report is always valuable, though they cost $100 to $200 or more, so may not be a good investment. You can also get a diamond appraisal to learn the details of your lab diamond and get an idea of its value — which may also cost you $100 to $200, potentially more than your item is worth.
Once you have the details of your diamond, assess the market. Do some googling for recent sales on ebay, Poshmark or other second-hand consigners where lab-grown diamonds are sold. Keep in mind that prices are dropping, so it is important the sales are recent.
Remember that the gold or platinum setting of your jewelry has market, spot value in addition to the stone.
As of , the spot gold value in the United States was trading at $ per ounce, or $ per gram.
As of April 20, 2025, the silver resale value in the United States was at $32.48 per ounce, or $1.15 per gram.
Lab-grown, synthetic diamonds FAQs
What you want to know about the pros and cons of lab-grown diamonds: physical properties, environmental impact, investment value and price trends:
What are lab-grown diamonds?
Lab-grown diamonds have the same chemical and physical properties as real diamonds, and are technically considered real diamonds.2
Also referred to as man-made diamonds, these stones are created using one of two methods:
- High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT)3: Using a small diamond seed crystal, the lab heats a chamber to as high as 1,600 degrees Celsius and applies pressure of 870,000 pounds per square inch. These two forces combined result in the diamond growing around the diamond seed.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)3: The diamond seed crystal sits in a chamber filled with carbon gas that's heated to 1,200 degrees Celsius. A microwave beam then creates a plasma cloud that deposits carbon precipitation onto the diamond seed, which grows into a diamond.
Both methods take place in a lab and replicate the process that occurs in nature to create real diamonds. While mined diamonds can take more than a billion years to form, the lab process takes just weeks to complete.
Are lab-grown diamonds real?
Despite public misconceptions that lab diamonds are artificial, there are no chemical or visual differences between lab-grown diamonds and earth-created diamonds.
In fact, gemologists have stopped using the word “synthetic” to describe lab-grown diamonds, since they have the same physical characteristics as natural diamonds. They are, however, man-made.
Gemologists use the same four “Cs” to grade both natural and lab-grown diamonds:
- Cut – Certain cuts, like round, are in higher demand and therefore more valuable
- Color – The less yellow a diamond appears, the more valuable it typically is
- Clarity – Fewer flaws and visible inclusions (mineral crystals inside a diamond), the higher quality
- Carat – The higher the carat weight, the more expensive
Lab-grown diamonds are also just as durable, with a 10 hardness level on the Mohs scale,4 which is used to identify minerals based on their scratch resistance.
This makes lab-grown diamonds higher quality than diamond simulants like moissanite, with a Mohs hardness rating of 9.25, or cubic zirconia, which has an 8-8.5 rating. Learn more about these “fake diamonds” and how they compare to lab and mined diamonds.
However, lab grown diamonds are still subject to the same color grading scale as natural diamonds. The highest grade is D (colorless), and the scale goes all the way to Z, though most diamonds on the market don’t go below J.
Fancy lab diamonds in yellow and blue are also popular and considered desirable on the resale market.
Just like natural diamonds, lab-grown diamonds vary in quality.
“Some lab-grown diamonds are tinted and have imperfections, but the most advanced are just as colorless and flawless as the highest quality natural diamonds,” Avi Levy, president of the International Gemological Institute, wrote in a press release.
Most man-made diamonds are large in size and high in quality. Needless to say, the diamond industry is struggling to stay relevant in the face of such excellent-quality competition.
What is the difference between lab-grown diamonds vs natural diamonds?
The only physical difference (besides how they’re made) between natural and lab-grown diamonds is that natural diamonds contain trace amounts of nitrogen, while lab-made diamonds do not.5
Nitrogen presence is the one identifying property gemologists use to distinguish the two in testing.
Every lab-grown diamond should also have a small inscription on the girdle — the area on a diamond that separates the bottom from the crown — indicating it was created in a lab, plus a report number. The inscription is microscopic, requiring a loupe or microscope to see.
Of course, the other big difference is that lab-grown diamonds are far less expensive than natural diamonds of similar quality — about a third less as of October 2023, though the value of both natural diamonds and LGD are on the decline.
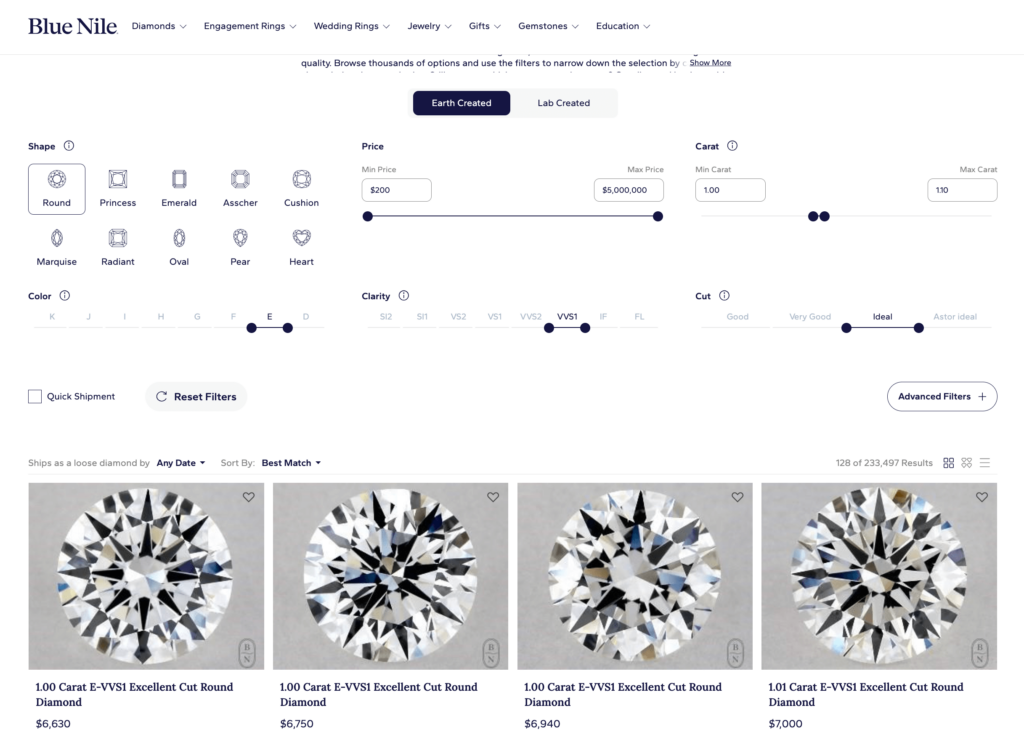
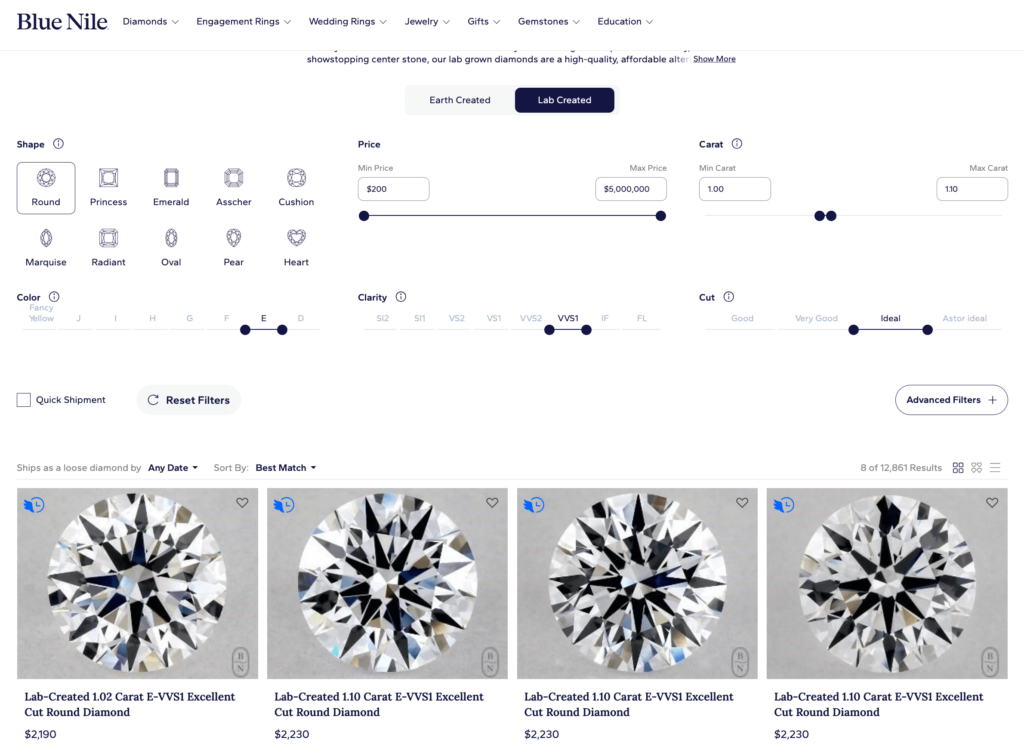
Here are some recent examples of round, 1-carat E, VSS1 lab-grown and natural diamonds for sale on BlueNile.com:
| Natural | Lab-created |
| ~$6,900 | ~$2,100 |
Natural diamonds:
Lab-created diamond for the same quality stone:
Are lab-grown diamonds more ethical than natural ones?
Lab-grown diamonds are considered more ethical than natural diamonds because of the lower environmental and humanitarian impact required to create them. Mining earth diamonds involves huge amounts of dirt removal, potential toxic water runoff, and air pollution.
Local communities in diamond-rich, but impoverished areas in southern Africa and Russia can also be negatively impacted by these environmental factors, and dangerous working conditions, as well as violent conflicts over the diamond trade.
In 2003, 59 nations signed the Kimberly Process,8 which aims to make the diamond trade more transparent and secure by requiring certification that diamonds are sourced in an ethical way, and are not in fact “conflict diamonds” or “blood diamonds.”
While it ensures conflict-free countries of export, diamonds may still be smuggled from conflict zones into conflict-free zones as a work-around, so it is nearly impossible to truly understand the origin of your stone.
Lab-grown diamonds, meanwhile are typically created much more ethically, even if their creation and shipping do consume environment-destroying fossil fuels.
One report9 underwritten by the De Beers group, which has a monopoly on the global natural diamond industry, wrote that the process to create lab-grown diamonds produced three-times the greenhouse gasses involved in mining the natural equivalent.
Are lab grown diamonds GIA certified?
Yes, the GIA has been grading lab-grown diamonds since 2007.
The Gemological Institute of America is the leading laboratory that provides certified reports on diamonds and gemstones verifying their qualities and estimated monetary value. Diamond certificates from the GIA and the International Gemological Institute and Gem Certification & Assurance Lab are very helpful in reselling any gemstone, and are required by some diamond buyers. A GIA certificate costs $100 to $200 for most diamonds.
As of 2020, the GIA offers full grading reports for lab-grown diamonds that are the same for mined diamonds.
Are lab-grown diamonds a good investment?
Neither lab-grown or most natural diamonds are good financial investment. The price of lab-grown diamonds continues to drop as supply grows. That means they are unlikely to increase in resale value.
RapNet Diamond Index is the industry standard for tracking diamond pricing, but does not include lab-grown diamonds in its report.
Founder Martin Rapaport has been vocal about his frustration with the growing lab diamond industry, penning a scathing memo in early 2023 calling on the industry to stop doing business in lab-grown diamonds.7
He recently spoke about lab diamond demand replacing mined diamond demand:
Lab-grown diamond prices are falling as supply continues to increase. More labs means more competition and lower prices for consumers. Unfortunately, that also impacts your ability to resell your lab-grown diamond ring in the future.
For instance, diamond company De Beers has dropped some of its natural diamond prices by 40% last year. Consumers used to see a 10% discount compared to natural diamonds, but now that price difference is as much as 80%.10
Natural diamond prices have also dropped significantly in recent years, in part because of the increased popularity and affordability of lab diamonds, as well as general lack of interest from consumers who no longer covet big, flashy diamonds as they did a few years ago:

“I recommend buying diamonds for their beauty, meaning, and durability, not as an investment,” says Ty Wilson, co-founder and COO of CustomMade, an online custom jewelry designer based in Cambridge, Mass. Same can be said for lab-grown or synthetic diamonds.
Will jewelers buy lab-grown diamonds?
Very few jewelers or diamond buyers buy lab-grown diamonds, but there are exceptions.
Some local jewelers may be willing to buy lab-grown diamonds for resale, especially if you originally purchased yours at that location. You may also be able to do a trade-in for another piece of jewelry instead of getting cash.
Keep in mind that diamonds of all kinds — natural and lab-grown — are depreciating in value in part because retailers have too much inventory.
Your safest bet is to resell the gold or platinum setting, which is always sellable. Gold prices have been strong for the past couple of years. Learn more about how to value your gold and where to sell it.
Diamonds USA buys all diamond sizes and quality — both natural and lab-grown. They also buy all gold, silver and platinum jewelry and scrap.
Bottom line: Understand the value of your lab-grown diamond before you sell
It's important to be realistic with your expectations before you start looking to sell your lab-grown diamond, as few jewelry buyers take them.
Get an appraisal or find your original paperwork to confirm the quality of your lab-grown diamond. The larger the stone, the easier time you'll have reselling it. It may help to focus on selling the precious metal in which the diamond is set.
Get a quick quote to sell your lab-grown diamond at Diamond USA now >>
SOURCES
- “The Knot 2023 Real Weddings Study,” Feb 14, 2024. The Knot. https://www.theknot.com/content/wedding-data-insights/real-weddings-study
- “Lab-Grown Diamonds FAQ,” International Gem Society. https://www.gemsociety.org/article/lab-grown-diamonds-faq/
- “HPHT and CVD Diamond Growth Processes: Making Lab-Grown Diamonds,” July 25, 2016. Gemological Institute of America. https://www.gia.edu/hpht-and-cvd-diamond-growth-processes
- “Mohs Hardness Scale,” National Park Service. https://www.nps.gov/articles/mohs-hardness-scale.htm
- “Is There a Difference Between Natural and Laboratory-Grown Diamonds?” May 31, 2019. Gemological Institute of America. https://www.gia.edu/gia-news-research/difference-between-natural-laboratory-grown-diamonds
- “The American Gem Registry,” American Gem Registry. https://americangemregistry.com/about-the-appraiser/
- “Industry-Insider Rapaport Lashes Out Against Lab-Grown Diamonds To No Avail,” Feb 8, 2023. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/pamdanziger/2023/02/08/industry-insider-rapaport-lashes-out-against-lab-grown-diamonds-to-no-avail
- “Working together to stem the tide of conflict diamonds worldwide,” The Kimberley Process. https://www.kimberleyprocess.com/en/participants
- “Total Clarity: The Realities of Modern Diamond Mining,” Diamond Producers Association, May 2, 2019 https://lucaradiamond.com/site/assets/files/4832/dpa_totalclarity_report_050219.pdf
- “Diamond demand is falling so fast—courtesy lab-grown stones—De Beers is cutting some prices by more than 40%,” Sept. 3, 2023. Fortune. https://fortune.com/2023/09/03/diamond-demand-falling-lab-grown-stones-de-beers-cutting-cutting-prices/

